Valpoi, Goa last week saw a case of Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), commonly known as monkey fever, detected.
Hospitalisation of an elderly woman for a brief period took place after she contracted this Fever. “The patient is doing well,” state epidemiologist Dr.Utkarsh Betodkar, said.
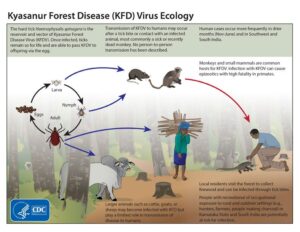
The first traces of the disease appeared at Kyasanur village near Sagar in Shivamogga district of Karnataka. Bandipur National Park (Chamarajnagar) and parts of the Nilgiris also had monkeys detected with traces of the virus.
Handling of dead, infected monkeys caused human infection in Bandipur. Wayanad in Kerala also detected a human carrier.
IN GOA
The Monkey Fever had first been detected in Sattari taluka in 2015. Some cases had also been detected in Bethora taluka earlier this year. This disease is the cause of the death of 3 persons and 277 cases were reported since then.
The Directorate of Health Services (DHS) undertook a vaccination programme in two talukas to control the infection, and many got the vaccinations. However, the DHS faced some problems with the programme.
The vaccine doses should be taken over a period of five years. The effort does not seem to have generated the expected result, and Betodkar said though people come forward to get vaccinated in the initial rounds, many don’t turn up for subsequent rounds of vaccination.
Since this problem, Betodkar said they issue health cards to people mentioning the dates on which they have to report to the health facility for the next vaccine dose.
“We will continue our propaganda to make people aware of the danger of KFD,” Betodkar said.
Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) is a tick-borne viral hemorrhagic fever endemic to South Asia. The disease is caused by a virus belonging to the family Flaviviridae, which also includes yellow fever and dengue fever.
SYMPTOMS OF MONKEY FEVER
- A high fever with frontal headaches
- Followed by hemorrhagic symptoms, such as bleeding from the nasal cavity, throat, and gums, as well as gastrointestinal (stomach & intestines) bleeding.
- Other symptoms include vomiting
- Muscle stiffness
- Tremors
- Absent reflexes
- Mental disturbances.
WAYS TO PREVENT THIS DISEASE
- KFDV Vaccination – consists of formalin-inactivated KFDV
- Protective clothing
- Tick control & mosquito control are advised.
- The vaccine has a 62.4% effectiveness rate for individuals who receive two doses. For individuals who receive an additional dose, the effectiveness increases to 82.9%.